A Comprehensive guide to Mobile Application Platforms
Table of Contents
- What is a Mobile Application Platform?
- Why Choosing the right mobile application platform can make or break your app?
- What are the key components of a mobile application platform?
- What are the different types of mobile application platforms?
- How to choose the best mobile application platform for your project?
- Understand Your Target Audience
- Evaluate the Type of App You’re Building
- Consider Development Resources and Expertise
- Budget and Cost Considerations
- Scalability and Future Growth
- Security Requirements
- Integration with Existing Systems
- App Store Policies and Distribution
- User Feedback and Iteration
- Long-Term Support and Viability
- Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
What is a Mobile Application Platform?
A mobile application platform is a comprehensive framework that allows developers to
create, deploy, and manage mobile apps across various devices and operating systems. These
platforms provide essential tools, libraries, and frameworks, enabling the development of
apps with ease and efficiency. Over the years, the rise of smartphones has spurred the growth
of mobile app platforms, making them crucial in the tech ecosystem.
In the early 2000s, mobile applications were basic, often restricted to specific devices. However, the launch of iOS and Android revolutionized the industry, introducing app stores and extensive development tools that made app creation accessible to a broader audience. Today, Android and iOS dominate the market, accounting for over 99% of global mobile operating system market share, according to StatCounter.
A robust mobile application platform offers cross-platform development capabilities, allowing apps to run seamlessly on different operating systems. This is particularly important given that mobile app usage continues to surge; as of 2024, there are over 7 billion mobile users worldwide, with the average person spending over 4 hours a day on their smartphone. The rapid growth in mobile users and their demand for high-quality apps have made mobile application platforms indispensable for businesses seeking to engage with their audience effectively. As technology evolves, these platforms will continue to play a pivotal role in the development and distribution of mobile applications.
Why Choosing the right mobile application platform can make or break your app?
As the demand for mobile applications continues to grow, the importance of selecting the right mobile application platform has become more evident than ever. These platforms are not just about coding tools; they encompass the entire ecosystem required to support the lifecycle of a mobile app, including development environments, APIs, testing frameworks, and app distribution channels. The decision on which platform to use can significantly impact an app’s performance, user experience, and market reach.
Historically, developers had to choose between building for either iOS or Android, or they faced the challenge of maintaining separate codebases for each operating system. This scenario often led to increased development costs and extended time-to-market. However, the advent of cross-platform frameworks like React Native and Flutter has changed the landscape. These frameworks allow developers to write code once and deploy it across multiple platforms, reducing costs and simplifying the update process. As of 2024, cross-platform apps account for around 40% of the mobile applications in the market, highlighting the growing trend toward efficiency and cost-effectiveness.
Moreover, the success of an app is often tied to the community and support surrounding a mobile application platform. Platforms like Android and iOS boast extensive developer communities, providing a wealth of resources, tutorials, and third-party tools that help developers overcome challenges quickly. This collaborative environment fosters innovation and ensures that even small development teams can produce high-quality, competitive apps. With the mobile app market projected to reach $781.70 billion in revenue by 2029, choosing the right platform is a critical decision that can determine the success or failure of a mobile application.
What are the key components of a mobile application platform?
A mobile application platform is a comprehensive environment that supports the entire lifecycle of a mobile app, from development to deployment and maintenance. To effectively serve developers and businesses, a mobile application platform must include several key components, each playing a vital role in ensuring that apps are built efficiently, perform well, and can be distributed and maintained effectively. Below are the key components of a mobile application platform:
1. Integrated Development Environment (IDE)
The IDE is the primary tool that developers use to write, test, and debug their applications. It often includes a code editor, a compiler or interpreter, and a debugger.
Examples: Xcode for iOS, Android Studio for Android, and Visual Studio for MAUI (formerly Xamarin).
Importance: A robust IDE streamlines the development process by providing tools and features like code autocompletion, syntax highlighting, and integrated testing environments. This allows developers to focus on writing code and solving problems rather than configuring their tools.
2. Software Development Kits (SDKs)
SDKs are a collection of software tools, libraries, documentation, and sample code that developers use to create applications for a specific platform.
Examples: Android SDK, iOS SDK.
Importance: SDKs provide developers with the necessary resources to access native features of a platform, such as cameras, GPS, and sensors. They also include APIs that simplify complex tasks like networking, data storage, and user interface design.
3. Application Programming Interfaces (APIs)
APIs are sets of protocols and tools that allow different software components to communicate with each other. In mobile application platforms, APIs are used to connect apps with external services or platform-specific features.
Examples: Google Maps API, Facebook Login API, Apple Pay API.
Importance: APIs enable developers to integrate third-party services and functionalities into their apps, such as social media sharing, payment processing, and cloud storage. This not only extends the capabilities of an app but also saves development time by leveraging existing solutions.
4. User Interface (UI) Frameworks
UI frameworks provide the tools and libraries needed to create the visual elements and layout of an app, including buttons, menus, and navigation structures.
Examples: SwiftUI for iOS, Jetpack Compose for Android, React Native for cross-platform development.
Importance: A good UI framework simplifies the process of designing and implementing user interfaces, ensuring that the app is both visually appealing and easy to use. These frameworks often include pre-built components that are optimized for performance and consistency across different devices.
5. Testing and Debugging Tools
These tools help developers identify and fix issues in their apps before they are released. They can simulate different devices, test app performance under various conditions, and detect bugs.
Examples: Xcode’s Simulator, Android Emulator, Appium for automated testing.
Importance: Testing and debugging tools are critical for ensuring that apps are stable, secure, and perform well across different devices and operating system versions. They help developers catch and fix issues early in the development process, reducing the risk of costly errors in production.
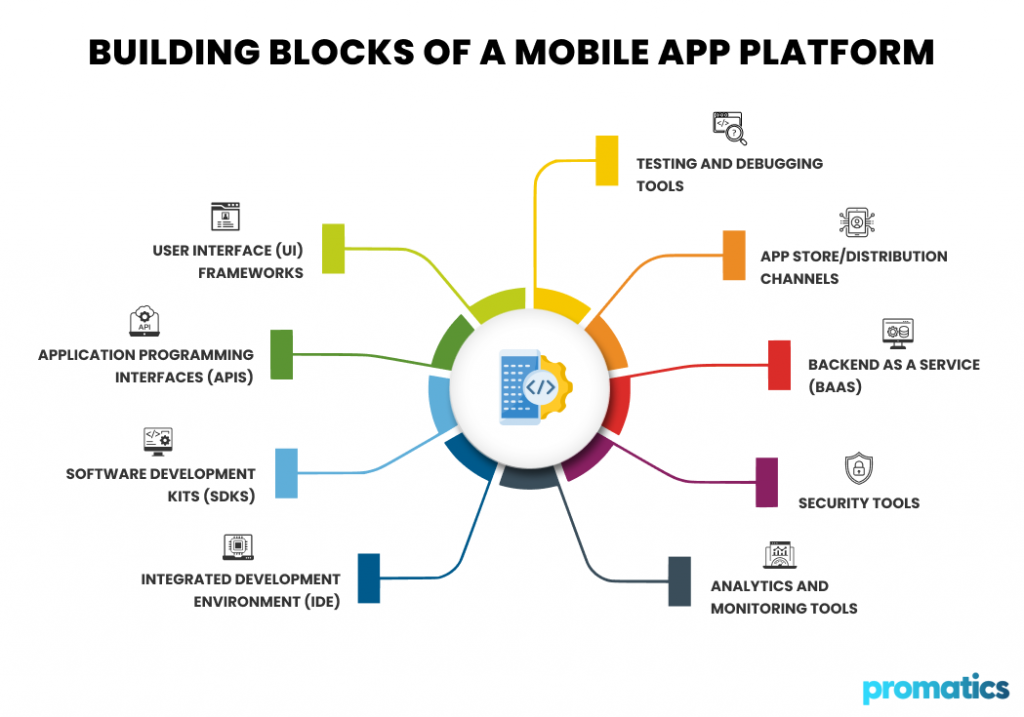
6. App Store/Distribution Channels
These are platforms where developers can publish their apps, making them available for download by users. They also handle app updates, user reviews, and monetization.
Examples: Apple App Store, Google Play Store.
Importance: Distribution channels are the primary way that apps reach users. They also provide valuable analytics and feedback that developers can use to improve their apps.
Additionally, app stores often enforce quality and security standards, ensuring that only safe and reliable apps are available to users.
7. Backend as a Service (BaaS)
BaaS platforms provide cloud-based backend services like data storage, user authentication, push notifications, and server management, which are essential for many mobile apps.
Examples: Firebase, AWS Amplify.
Importance: BaaS simplifies backend development by offering ready-to-use services that scale with app demand. This allows developers to focus on frontend development and user experience, rather than managing servers and databases.
8. Security Tools
Security tools are used to protect apps from threats like data breaches, unauthorized access, and malware.
Examples: SSL/TLS encryption, OAuth for secure authentication, mobile security suites like AppScan.
Importance: Security is a top priority for mobile apps, especially those handling sensitive user data. Security tools help ensure that apps comply with industry standards and regulations, protecting both the developer and the end-user.
9. Analytics and Monitoring Tools
These tools provide insights into how users interact with an app, tracking metrics such as user engagement, retention rates, and in-app behavior.
Examples: Google Analytics for Firebase, Mixpanel.
Importance: Analytics and monitoring tools for apps are essential for understanding user behavior and making data-driven decisions to improve app performance and user satisfaction.
Each of these components is crucial in building, deploying, and maintaining high-quality mobile applications. By providing a comprehensive suite of tools and resources, mobile application platforms empower developers to create apps that are not only functional and secure but also capable of reaching a wide audience and adapting to evolving user needs.
What are the different types of mobile application platforms?
Mobile application platforms can be categorized into several types based on their underlying technology and the environments they support. Each type has its own advantages and disadvantages, making it suitable for different kinds of projects and business needs. Here are the main types of mobile application platforms:
1. Native Platforms
Native platforms involve developing apps specifically for a single operating system, such as iOS or Android. These apps are written in languages that are native to the platform—Swift or Objective-C for iOS, and Java or Kotlin for Android.
Examples of Native Platforms
- iOS: Apple’s native platform for iPhone and iPad apps. Apps are developed using Swift or Objective-C in Xcode.
- Android: Google’s native platform for Android devices. Apps are developed using Java or Kotlin in Android Studio.
Advantages:
- Superior performance due to direct access to device hardware and system resources.
- Enhanced user experience as the apps are optimized for the specific platform.
- Full access to all native APIs and features.
Disadvantages:
- Higher development costs due to maintaining separate codebases for each platform.
- Increased time-to-market when developing for multiple platforms.
2. Cross-Platform Development Platforms
Cross-platform development platforms allow developers to write code once and deploy it on multiple platforms, such as iOS, Android, and sometimes even web. Popular frameworks include React Native, Flutter, and Xamarin.
Examples of Cross-Platform Development Platforms
- React Native: Developed by Facebook, React Native allows developers to build mobile apps using JavaScript and React, with a single codebase that runs on both iOS and Android. React Native app development remains the most popular form of building cross platform apps worldwide.
- Flutter: Created by Google, Flutter uses the Dart programming language and allows developers to create natively compiled applications for mobile, web, and desktop from a single codebase.
- .NET MAUI: Owned by Microsoft, .NET MAUI is the successor of Xamarin and uses C# and .NET, allowing developers to build cross-platform apps for iOS, Android, and Windows.
Advantages:
- Cost-effective and time-saving, as a single codebase serves multiple platforms.
- Easier maintenance and updates across platforms.
Disadvantages:
- May not offer the same level of performance or access to native features as native apps.
- User experience might not be as polished compared to native apps.
3. Hybrid Platforms
Hybrid platforms blend elements of native and web apps. They are built using web technologies like HTML, CSS, and JavaScript and are wrapped in a native container that allows them to be deployed as mobile apps. Frameworks like Apache Cordova and Ionic are popular for hybrid development.
Examples of Hybrid Platforms
- Apache Cordova: An open-source mobile development framework that allows developers to use standard web technologies—HTML, CSS, and JavaScript—to create apps that can be installed on various platforms.
- Ionic: A popular hybrid platform that builds on top of Apache Cordova and Angular. Ionic allows developers to create apps with a single codebase that can be deployed across multiple platforms.
Advantages:
- Faster development and easier to build for multiple platforms.
- Can leverage web development skills and tools.
Disadvantages:
- Performance is inferior to native or even cross platform apps.
- Limited access to native device features and less optimized user experience.
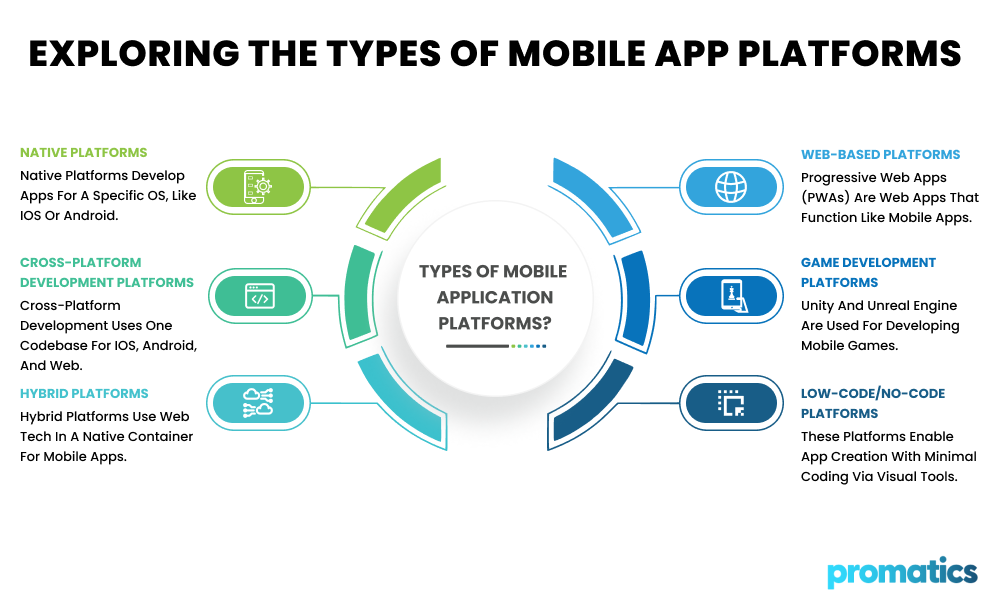
4. Web-Based Platforms (Progressive Web Apps – PWAs)
Progressive Web Apps or PWA is a web applications that behave like a mobile app. They run in a web browser but offer features like offline access, push notifications, and the ability to be installed on a device’s home screen.
Examples of Web-Based Platforms
- Google Lighthouse: A tool by Google that helps developers build Progressive Web Apps (PWAs). PWAs run in a web browser but offer app-like experiences.
- Workbox: Another Google tool that simplifies the creation of PWAs by handling caching, routing, and other key functionalities.
Advantages:
- No need for app store distribution, which can simplify the release process.
- Works across all devices and platforms with a single codebase.
Disadvantages:
- Limited access to native device features compared to native or hybrid apps.
- Performance may not match that of native or cross-platform apps.
5. Game Development Platforms
Specialized platforms and engines like Unity and Unreal Engine are used to develop mobile games. These platforms offer tools and libraries specifically designed for creating high-performance, interactive games.
Examples of Game Development Platforms
- Unity: A widely-used game development engine that allows developers to create 2D, 3D, and VR games for various platforms, including mobile (iOS and Android), consoles, and PCs.
- Unreal Engine: Developed by Epic Games, Unreal Engine is a powerful game development platform known for its high-quality graphics and is used to create both mobile and console/PC games.
- Cocos2d-x: Open-source game engine for creating 2D and 3D games.
Advantages:
- Optimized for graphics-intensive applications and games.
- Access to a wide range of tools and resources for game development.
Disadvantages:
- Not ideal for non-gaming applications due to their specialized focus.
Each type of mobile application platform has its own set of strengths, making them more or less suitable depending on the project’s specific needs, budget, and target audience.
6. Low-Code/No-Code Platforms
These platforms allow users to create apps with minimal or no coding knowledge. They use visual interfaces and pre-built components to assemble apps.
Examples of Low code/ No code app development platforms
- Appy Pie: Offers a drag-and-drop interface for building various types of apps.
- BuildFire: Focuses on mobile app development with a user-friendly interface.
- Mendix: Enterprise-grade platform for complex app development.
Advantages:
- Faster Development Time: No-code/low-code platforms significantly speed up the development process by allowing users to build apps using pre-built templates, drag-and-drop interfaces, and visual tools.
- Lower Development Costs: These platforms reduce the need for extensive coding expertise, enabling non-developers or small teams to create applications.
Disadvantages:
- Limited Customization: No-code/low-code platforms often come with predefined templates and components, which can limit the level of customization available. For complex or highly specific applications, this lack of flexibility can be a significant drawback.
- Scalability and Performance Issues: Applications built on no-code/low-code platforms may face scalability challenges, especially as the app grows in complexity or user base. Additionally, because these platforms often abstract away the underlying code, performance optimization may be harder to achieve.
How to choose the best mobile application platform for your project?
Choosing the best mobile application platform for your project is a critical decision that can significantly impact the success of your app. The right platform can streamline development, reduce costs, and ensure your app reaches the intended audience effectively. Here are key factors to consider when selecting the most suitable mobile application platform for your project:
1. Understand Your Target Audience
- Platform Popularity: Build for android or iOS? Research which platforms are most popular among your target audience. For example, iOS tends to be more popular in North America and Western Europe, while Android dominates in regions like Asia, Africa, and Latin America.
- Demographics: Consider the demographics of your users, including age, income level, and device preference. For instance, iOS users are often associated with higher income brackets and tend to spend more on apps and in-app purchases.
- User Behavior: Analyze how your target audience interacts with mobile apps. If they prioritize performance and smooth user experience, a native platform might be the best choice.
2. Evaluate the Type of App You’re Building
- Complexity and Features: If your app requires intensive use of device features (e.g., camera, GPS, AR), a native platform like iOS or Android might be preferable due to its better access to hardware and performance optimization.
- User Experience: If delivering the best possible user experience is crucial, native development might be the way to go. Cross-platform and hybrid apps may offer a slightly less polished user experience but can still be sufficient for less complex apps.
- Development Timeline: If you need to get your app to market quickly and on multiple platforms, cross-platform tools like React Native or Flutter can be ideal, as they allow you to build once and deploy across iOS and Android.
3. Consider Development Resources and Expertise
- Team Expertise: Assess your team’s familiarity with the platform. If your developers are well-versed in a particular language or framework (e.g., Swift for iOS or Java for Android), it might make sense to leverage that expertise.
- Availability of Resources: Ensure that the platform you choose has ample documentation, tutorials, and a strong developer community. This support can be invaluable in troubleshooting issues and speeding up development.
4. Budget and Cost Considerations
- Development Costs: Native apps generally require separate codebases for iOS and Android, leading to higher development costs. Cross-platform or hybrid solutions can reduce these costs by allowing code reuse.
- Maintenance Costs: Consider the long-term app maintenance costs. Cross-platform apps are easier and cheaper to maintain, as updates can be applied to both platforms simultaneously.
- Licensing and Tools: Factor in the cost of any necessary development tools, licenses, or third-party services required by the platform.
5. Scalability and Future Growth
- Platform Flexibility: Choose a platform that can grow with your app. For instance, if you plan to add complex features or scale the app significantly in the future, a platform with strong support for continuous integration and development (CI/CD) might be essential.
- Market Trends: Keep an eye on emerging trends in mobile development. Platforms like Flutter are gaining popularity due to their performance and flexibility, which might make them a good long-term investment.
6. Security Requirements
- Data Sensitivity: If your app will handle sensitive user data (e.g., financial information, personal health data), ensure the platform has robust security features. Native platforms often offer better security options, but cross-platform frameworks are also catching up.
- Compliance: Ensure the platform supports compliance with necessary regulations like GDPR, HIPAA, or PCI DSS.
7. Integration with Existing Systems
- Backend Compatibility: Consider how well the platform integrates with your existing backend systems. Some platforms, like those using Backend as a Service (BaaS), offer seamless integration with cloud services, which can simplify development.
- Third-Party Services: If your app will rely heavily on third-party APIs or services (e.g., payment gateways, analytics), ensure the platform supports easy integration with these services.
8. App Store Policies and Distribution
- Approval Process: Each platform’s app store has different approval processes and policies. For example, Apple’s App Store has stricter guidelines than Google Play, which might impact your development timeline.
- Monetization Options: Consider how you plan to monetize your app (e.g., in-app purchases, ads) and whether the platform supports your chosen monetization model effectively.
9. User Feedback and Iteration
- Testing and Iteration: If your project involves frequent updates or relies on user feedback, consider platforms that support rapid iteration and testing. Cross-platform tools are often better suited for this due to their single codebase.
10. Long-Term Support and Viability
- Platform Longevity: Choose a platform that is actively maintained and likely to be supported in the long term. The last thing you want is to invest in a platform that becomes obsolete.
- Community and Ecosystem: A vibrant developer community and ecosystem around the platform can be a strong indicator of its longevity and support.
Selecting the best mobile application platform requires a thorough understanding of your project’s requirements, your audience, and your development resources. By carefully evaluating the factors outlined above, you can make an informed decision that aligns with your project goals and maximizes your app’s potential for success.
Frequently Asked Questions
Q1. Which is the best mobile application platform?
The best mobile app platform depends on the target audience and goals. iOS is preferred for high-quality user experience and monetization, while Android offers broader global reach and customization. Cross-platform tools like Flutter or React Native provide versatility, making it easier to develop for both platforms efficiently.
Q2. What are the key differences between native and cross platform mobile application platforms?
Native app development involves building apps specifically for a platform (iOS or Android) using platform-specific languages like Swift for iOS and Kotlin for Android. It offers better performance, access to device features, and a smoother user experience.
Cross platform app development, on the other hand, uses web technologies like HTML, CSS, and JavaScript wrapped in frameworks like React Native or Flutter. Cross platform apps are cross-platform, reducing development time and cost.
Q3. How do Flutter and React Native compare in terms of performance and development ease?
Flutter and React Native are both popular for cross-platform app development, but they differ in performance and development ease. Flutter uses Dart and compiles directly to native code, offering near-native performance, smooth animations, and efficient UI rendering. React Native uses JavaScript and a bridge to communicate with native components, which can sometimes result in slower performance for complex apps. React Native benefits from JavaScript’s popularity and large community support, making it easier for many developers to learn. Flutter, with its widget-based approach and hot-reload feature, offers a smooth, consistent development experience but has a smaller learning curve.
Q4. How does Promatics can help build you a great app in Flutter or React Native mobile application platform?
Promatics specializes in building high-quality mobile apps using Flutter and React Native by offering tailored solutions, fast development cycles, and cross-platform functionality. Our expertise ensures seamless performance, user-friendly designs, and cost-efficient development, helping businesses reach both iOS and Android audiences with a single codebase.
Q5. How to choose the right mobile application platform for your project?
Choosing the right mobile application platform involves assessing your project’s needs, target audience, and budget. Consider iOS for premium user experience, Android for broader reach, or cross-platform solutions like Flutter or React Native for cost efficiency and wider coverage. Evaluate factors like performance, development time, and access to device features to make an informed decision.
Still have your concerns?
Your concerns are legit, and we know how to deal with them. Hook us up for a discussion, no strings attached, and we will show how we can add value to your operations!
